The Evolution of Residential Security Solutions
Residential security solutions have evolved significantly over the decades, reflecting broader societal changes and technological advancements.
Early Security Measures
Initially, residential security relied heavily on physical barriers such as locks, fences, and gates. These measures were fairly effective but could be easily bypassed by experienced intruders.
Introduction of Alarm Systems
In the mid-20th century, alarm systems became more common in homes. These systems included motion detectors, door and window sensors, and audible alarms to alert homeowners and neighbors of possible intrusions. Although these systems improved security, they often resulted in false alarms and provided real-time response challenges.
Advent of CCTV Technology
Starting in the 1960s, Closed-Circuit Television (CCTV) technology began to be used for residential security. The concept of monitoring and recording potential intruders added a significant layer of security. Early CCTV systems were expensive and required significant technical expertise to install and maintain, limiting their widespread adoption.
Digital Transition
The transition to digital technology in the late 20th and early 21st centuries revolutionized residential security cameras. Digital cameras offered higher resolution, better storage solutions, and easier scalability. This made security camera systems more accessible and effective for average homeowners.
Modern Comprehensive Security Networks
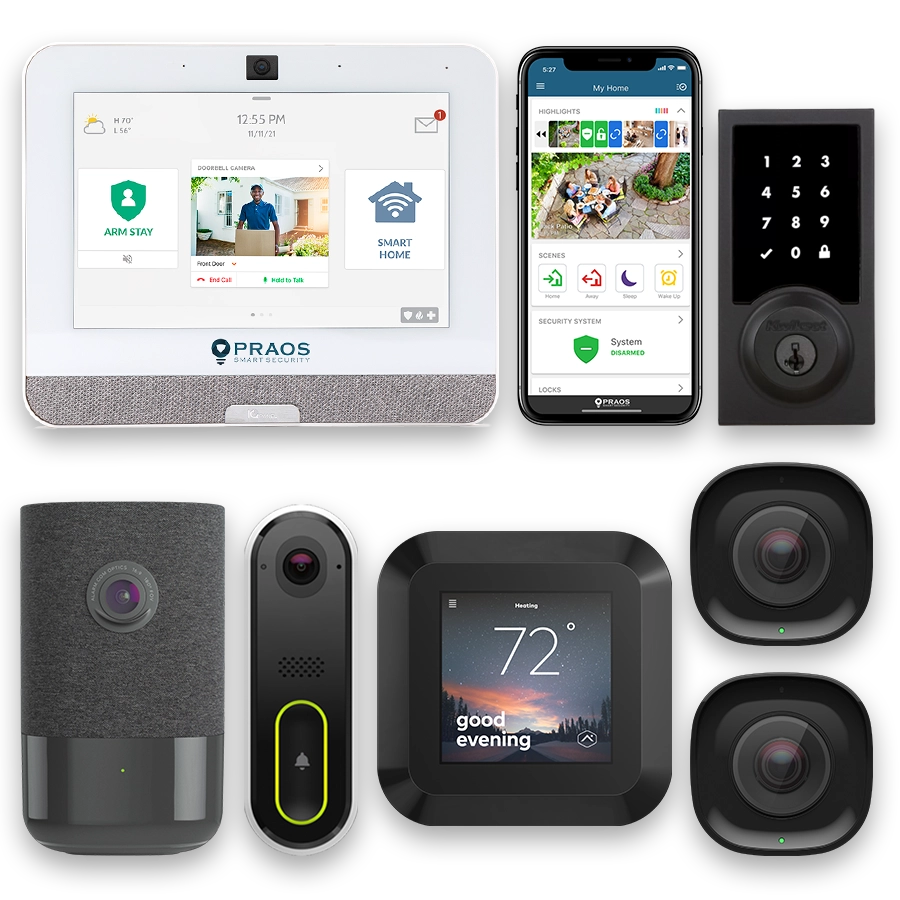
Today, comprehensive security camera networks have become an integral part of modern residential security solutions. These systems integrate multiple cameras, provide live video monitoring, automate alerts, and can store vast amounts of data on-cloud or local servers.
Key Milestones in the Evolution of Residential Security
| Time Period | Development |
|---|---|
| Early 20th Century | Physical barriers and basic lock-and-key mechanisms. |
| Mid 20th Century | Introduction of residential alarm systems with basic motion and entry sensors. |
| 1960s | Early adoption of CCTV technology for home security. |
| Late 20th Century | Digital security systems with enhanced image quality and data storage. |
| 21st Century | Integrated security networks with smart capabilities and real-time monitoring. |
Technological Advancements in Security Cameras
Technological advancements have significantly improved the performance and reliability of security cameras, making them an integral component of modern residential safety. Understanding these advancements helps homeowners make informed decisions about their home security systems.
High-Resolution Imaging
One of the most notable advancements in security camera technology is the development of high-resolution imaging. Cameras now offer resolutions ranging from HD (720p) to 4K (2160p) and beyond. This increase in resolution provides clearer and more detailed images, which can be crucial for identifying intruders or other security-related incidents.
Enhanced Night Vision
Modern security cameras are equipped with advanced night vision capabilities. Infrared (IR) technology allows cameras to capture clear images in complete darkness. Some cameras also use color night vision, which combines low-light sensors with artificial lighting to produce more detailed images.
Smart Detection Features
Newer security cameras come with smart detection features, such as:
- Motion Detection: Cameras can detect and record movement in their field of view.
- Facial Recognition: Advanced algorithms can differentiate between known individuals and strangers.
- Object Detection: Some systems can identify specific types of objects, like packages or vehicles.
Cloud Storage & Access
Cloud storage solutions have revolutionized how video footage is stored and accessed. Instead of relying on local storage devices, which can be vulnerable to damage or theft, footage is stored securely on the cloud, offering several benefits such as:
- Remote Access: Homeowners can view live feeds and recorded footage from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Scalability: Cloud storage can be easily scaled to accommodate varying amounts of footage.
- Data Security: Cloud services offer encrypted storage to protect against unauthorized access.
Integration with Other Systems
Security cameras are increasingly being designed to integrate seamlessly with other smart home technologies. Integration can improve the functionality and efficiency of home security systems. Examples include:
- Smart Locks: Cameras can trigger locks to engage when they detect unusual activity.
- Home Automation: Cameras can work with lighting systems to illuminate areas when motion is detected.
- Voice Assistants: Integration with devices like Amazon Echo or Google Home allows for voice-activated security controls.
Advancements in Data Processing
Data processing capabilities have advanced significantly, allowing for real-time analysis and alerts. Edge computing enables cameras to process data locally, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. This means quicker response times and more efficient monitoring.
Comparison of Key Features in Modern Security Cameras
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| High-Resolution Imaging | Provides clearer, more detailed images |
| Enhanced Night Vision | Allows clear imaging in low-light conditions |
| Smart Detection Features | Includes motion, facial, and object detection |
| Cloud Storage & Access | Offers remote viewing and scalable storage |
| Integration with Other Systems | Works with smart home devices for enhanced functionality |
| Data Processing Capabilities | Enables real-time analysis and quicker response |
Designing an Effective Home Security Camera Network
When designing an effective home security camera network, it is essential to consider several key factors, including camera placement, coverage areas, types of cameras, and system integration. By taking a structured approach, homeowners can create a robust security system that enhances the safety and security of their property.
Camera Placement and Coverage
Proper camera placement is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of a home security network. Cameras should be strategically installed to cover all vulnerable points, such as entrances, driveways, and blind spots. Commonly recommended areas for camera installation include:
- Front Door
- Backyard and Side Gates
- Driveway
- Windows facing away from the street
- Interiors focusing on key entry points
Types of Cameras
Various types of cameras are available for home security, each with its unique features and benefits. Common types include:
- Bullet Cameras: Known for their long, cylindrical shape, these cameras are suitable for outdoor use and provide a deterrent effect.
- Dome Cameras: Typically installed indoors, their dome shape makes it difficult to determine the camera’s direction, offering a wider coverage area.
- PTZ Cameras: (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) Highly versatile and capable of remote directional and zoom control, useful for monitoring larger areas.
- Wireless Cameras: Easy to install and can be placed in more flexible locations since they do not require extensive wiring.
System Integration
Modern security camera networks should integrate seamlessly with other home security and smart home systems. This integration can include:
- Connecting cameras to alarm systems
- Incorporating motion detectors and sensors
- Using smart home hubs to control and monitor cameras remotely
Network Security
Ensuring the security of the camera network itself is as important as the physical installation. Using encrypted connections, regular software updates, and strong passwords can help protect against unauthorized access.
| Camera Type | Primary Use |
|---|---|
| Bullet Cameras | Outdoor, visible deterrent |
| Dome Cameras | Indoor, wide area coverage |
| PTZ Cameras | Large area monitoring with remote control |
| Wireless Cameras | Flexible installation indoors or outdoors |
By considering these elements, homeowners can design a comprehensive and effective security camera network that provides enhanced safety and peace of mind.
Privacy and Ethical Considerations in Surveillance
When implementing comprehensive security camera networks in residential areas, it is crucial to consider privacy and ethical implications. Awareness of these considerations helps to balance the need for security with the respect for individuals’ privacy rights.
Legal Framework
Each country or region typically has specific regulations governing the use of surveillance cameras. For example, in the United States, homeowners must comply with both federal and state laws regarding video recording. The Federal Wiretap Act restricts audio recording without consent, while state laws vary significantly regarding video capture within private properties.
In Europe, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes stringent requirements on the data collected through surveillance. Homeowners must ensure that their use of security cameras complies with principles of data protection, which include purpose limitation, data minimization, and transparency.
Transparency and Notification
Transparency is a cornerstone of ethical surveillance practices. Residents in areas under surveillance should be notified about the presence of cameras. Visible signs indicating the use of security cameras can serve to inform visitors and residents alike. Such practices not only enhance ethical compliance but also deter potential criminal activities.
Minimizing Intrusion
Designing the surveillance system to minimize intrusion into private areas is another essential consideration. Cameras should be positioned to monitor entry points and public spaces like driveways and front yards, while avoiding areas where individuals have a reasonable expectation of privacy, such as windows and backyards.
Advanced technologies, such as privacy masking features in cameras, can help to blur out specific parts of the video feed to protect sensitive areas. This ensures that the security objectives are met without overstepping privacy boundaries.
Data Security
Data collected by security cameras must be managed securely to prevent unauthorized access or breaches. Implementing robust encryption methods and secure data storage solutions is essential. Homeowners should regularly update firmware and use strong, unique passwords for their security systems.
Balancing Security and Privacy
Striking a balance between security and privacy involves ongoing assessment and adjustments. A one-size-fits-all approach does not apply, and every residential area may require a tailored strategy. Continuous dialogue within communities about surveillance can foster a mutual understanding and agreement on the ethical use of security technologies.
Vigilance in addressing privacy and ethical considerations ensures not only legal compliance but also the trust and comfort of residents. Well-implemented surveillance networks that respect privacy can significantly enhance the safety and quality of life in modern residential areas.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Security Camera Systems
The decision to invest in a comprehensive security camera network for residential areas involves a careful cost-benefit analysis. Homeowners must weigh the initial, and ongoing expenses against the potential advantages offered in terms of enhanced security and peace of mind.
One of the primary costs associated with security camera systems is the initial purchase and installation. Quality security cameras range in price, with more advanced models offering features such as high-definition video, night vision, and motion detection costing more. According to market data, homeowners can expect to spend anywhere from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on the complexity and sophistication of the system.
In addition to the initial costs, there are ongoing expenses to consider. These may include:
- Subscription Fees: Many security camera systems offer cloud storage services, which come with monthly or annual fees.
- Maintenance Costs: Regular upkeep, such as cleaning lenses and updating software, is necessary to ensure optimal performance.
- Electricity Usage: Although individual cameras consume relatively little power, the total energy cost can add up, especially in large networks.
Despite these costs, the benefits of a comprehensive security camera network can be substantial. Crime Deterrence is one of the most significant advantages. Studies have shown that visible security cameras can reduce the likelihood of property crimes such as burglary and vandalism. For instance, a study by the University of North Carolina found that 60% of convicted burglars stated the presence of cameras would deter them from targeting a home.
Moreover, security camera systems provide invaluable evidence for law enforcement in the event of a crime. High-definition recordings can help police understand the sequence of events, identify suspects, and potentially recover stolen property. This capability not only aids in the resolution of crimes but also serves as a powerful deterrent.
Another key benefit is remote monitoring and peace of mind. Many modern security camera systems offer remote access via smartphones or other devices, allowing homeowners to monitor their property in real-time from anywhere in the world. This feature is particularly valuable for frequent travelers and individuals with second homes.
Insurance benefits should also be taken into account. Many insurance companies offer discounts on homeowners’ insurance premiums for properties equipped with security systems, including comprehensive camera networks. This can partially offset the costs of the system over time.
When evaluating the overall value, it is essential to consider long-term benefits. The initial investment in a security camera network can enhance a home’s overall security, potentially increase its resale value, and provide continuous returns in terms of safety and peace of mind.
In conclusion, while the up-front and ongoing costs of installing a comprehensive security camera system can be significant, the potential benefits in terms of crime deterrence, evidence collection, remote monitoring, insurance discounts, and overall safety make it a worthwhile investment for many homeowners. A thorough cost-benefit analysis, tailored to individual needs and circumstances, is essential in making an informed decision.
Integration with Smart Home Technology
Integrating security camera networks with smart home technology represents a significant advancement in residential security. This collaboration enhances not only the security aspects but also the overall convenience for homeowners. Smart home technology enables seamless interaction between various home systems, providing an interconnected and streamlined experience.
The Role of Smart Home Hubs
Smart home hubs act as the central point of control, allowing homeowners to manage security cameras along with other smart devices. Popular hubs like Amazon Echo, Google Home, and Apple HomeKit can integrate with various brands and models of security cameras.
- **Amazon Echo** – Uses Alexa for voice control, compatible with cameras like Ring and Arlo.
- **Google Home** – Utilizes Google Assistant, integrates with Nest cameras and Wyze cameras.
- **Apple HomeKit** – Leverages Siri, works with brands like Eufy and Logitech Circle.
Features Enhanced by Integration
Security cameras, when integrated with smart home systems, offer enhanced features and functionalities:
- Unified Control Interface: Manage and monitor security cameras alongside other smart devices through a single app or voice commands.
- Automated Actions: Set triggers for cameras to record when other smart sensors are activated (e.g., motion detectors).
- Remote Access: View live footage and receive alerts while away from home via smartphone apps.
- Data Synchronization: Combine video data with other smart device logs for comprehensive security records.
Case Studies of Integration
Studies have shown that integration of security camera networks with smart home technology significantly increases user satisfaction and security system effectiveness. Below is a comparison of features between standalone security cameras and those integrated with smart home systems:
| Feature | Standalone Security Camera | Smart Home Integrated Camera |
|---|---|---|
| Remote Monitoring | Available | Available |
| Voice Control | Not Available | Available |
| Automated Triggers | Limited | Advanced |
| Unified App Control | No | Yes |
Challenges and Considerations
While integration offers many benefits, there are challenges to consider:
- Compatibility: Not all security cameras are compatible with every smart home hub, requiring careful selection.
- Privacy Concerns: Increased data collection necessitates robust privacy protections.
- Complexity: Integrating multiple devices adds to the complexity of setup and maintenance.
Conclusion
Integration with smart home technology significantly enhances the functionality and user experience of home security camera networks. While challenges exist, the benefits of unified control, advanced automation, and enhanced security demonstrate the value of this synergy in modern residential areas.
Future Trends in Residential Security Technology
The realm of residential security is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing consumer needs. The future trends in residential security technology indicate a shift toward more integrated, intelligent, and user-friendly systems.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
One of the most significant trends is the incorporation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in security systems. AI-driven cameras can distinguish between different types of motion, such as humans, animals, or vehicles, thus reducing false alarms. As these technologies continue to evolve, future security systems will offer increasingly accurate threat detection capabilities.
Cloud Storage and Data Analysis
The transition to cloud-based storage and data analysis is another emerging trend. Cloud storage allows for seamless access to video footage from anywhere with an internet connection, providing homeowners with greater flexibility and convenience. Additionally, cloud-based analytics can offer real-time insights and alerts, significantly enhancing the effectiveness of security measures.
Interconnected Smart Home Devices
The integration of security systems with smart home devices will continue to deepen. This interconnectivity allows for more comprehensive home automation and security solutions that work together cohesively. For example, security cameras can be synchronized with smart locks, lighting, and alarm systems to create a robust, unified security network.
Voice Control and User Interfaces
Voice control via assistants like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri is becoming increasingly popular. Future security systems are likely to offer enhanced voice-activated features, allowing users to control their security systems more intuitively. Improved user interfaces will also make these systems easier to operate, even for those who are not technologically savvy.
Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication methods, such as facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, and retina scans, are poised to become more prevalent in residential security. These methods provide a higher level of security compared to traditional passwords or PIN codes, offering homeowners peace of mind and reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The integration of security systems with the Internet of Things (IoT) presents numerous possibilities for enhanced functionality. IoT-enabled devices can communicate with each other to provide a holistic security solution that extends beyond just surveillance. For example, IoT sensors can detect environmental changes like smoke or gas leaks and trigger appropriate responses, integrating with fire alarms and notification systems.
5G Connectivity
The rollout of 5G networks is set to revolutionize residential security technology. With higher speeds and lower latency, 5G will enable faster and more reliable transmission of high-quality video feeds. This advancement will also support more connected devices within the home, making comprehensive security networks more feasible and effective.
Conclusion
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities and features of residential security systems. The trends highlighted above indicate a future where security solutions are more integrated, intelligent, and user-friendly, providing homeowners with enhanced protection and greater peace of mind.